Prefabricated Homes – Affordable and Efficient Housing Options with Fast Installation
Prefabricated homes represent a revolutionary approach to residential construction, offering homeowners a faster, more cost-effective alternative to traditional building methods. These factory-built structures combine quality craftsmanship with streamlined production processes, delivering complete housing solutions that can be assembled on-site in a fraction of the time required for conventional construction.
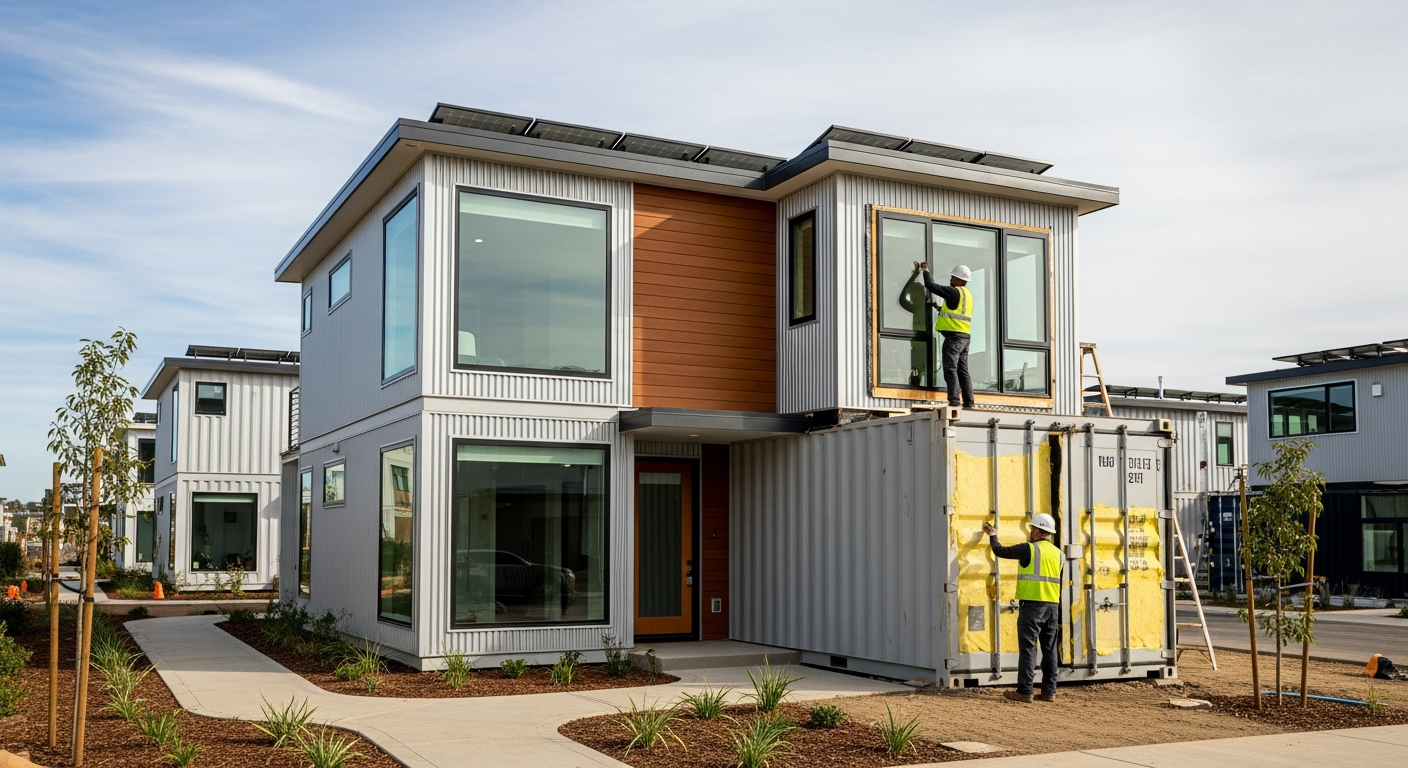

Prefabricated homes have emerged as a viable housing solution for individuals and families seeking efficiency, affordability, and modern design. Unlike traditional construction, these homes are manufactured in controlled factory settings, which minimizes weather-related delays and allows for precise quality management. Once completed, the sections are transported to the building site and assembled, often within days or weeks rather than months.
What Defines Prefabricated Homes and Their Construction Process?
Prefabricated homes are structures built in sections at manufacturing facilities before being transported to their final location for assembly. The construction process typically involves designing the home, manufacturing wall panels, roof trusses, and floor systems in a factory, and then shipping these components to the site. Workers then assemble the sections on a prepared foundation, connect utilities, and complete finishing work. This method contrasts sharply with traditional stick-built homes, where all construction occurs on-site. The controlled environment of a factory allows for consistent quality checks, reduced material waste, and protection from weather conditions that often delay conventional builds. Manufacturing timelines for prefabricated homes generally range from several weeks to a few months, depending on complexity and customization.
Comparing Efficient Prefabricated Homes with Traditional Building Methods
When evaluating prefabricated homes against traditional construction, several factors come into play. Traditional building methods involve purchasing land, hiring contractors, and constructing the home entirely on-site, which typically takes six months to over a year. Prefabricated homes, by contrast, can be completed in as little as three to four months from order to move-in. Quality control is another distinction: factory settings enable consistent inspections at each production stage, while on-site construction faces variables like weather, labor availability, and material delivery schedules. Energy efficiency often favors prefabricated homes due to tighter construction tolerances and modern insulation techniques standard in factory production. However, traditional builds offer greater flexibility for mid-construction changes, whereas prefabricated designs require more upfront planning.
Exploring Available Prefabricated Home Designs and Customization Options
Prefabricated homes come in diverse styles, from compact single-story layouts to expansive multi-level designs. Manufacturers offer base models that buyers can customize with various floor plans, exterior finishes, interior fixtures, and energy-efficient upgrades. Common design categories include modular homes (built in sections), panelized homes (wall panels assembled on-site), and manufactured homes (built to HUD code standards). Customization options typically include choosing kitchen layouts, bathroom configurations, flooring materials, window placements, and roofing styles. Some manufacturers provide architectural design services to create fully custom prefabricated homes that reflect individual preferences while maintaining the efficiency of factory production. Buyers should review portfolios from multiple manufacturers to understand the range of aesthetic and functional possibilities available.
Understanding Zoning Laws and Building Codes for Prefabrication
Navigating zoning regulations and building codes is essential when considering prefabricated homes. Local zoning laws dictate where homes can be placed, minimum lot sizes, setback requirements, and aesthetic standards that may affect prefabricated structures. Building codes ensure homes meet safety, structural, and energy efficiency standards. Modular and prefabricated homes built to local or state building codes are generally treated the same as traditional homes for permitting purposes. However, manufactured homes built to federal HUD standards may face different zoning restrictions in some communities. Prospective buyers should consult local planning departments early in the process to verify that their chosen prefabricated home design complies with applicable regulations. Some areas have specific restrictions on prefabricated housing, while others actively encourage it as a solution to housing shortages.
Key Advantages of Prefabricated Homes in the Modern Housing Market
Prefabricated homes offer several advantages that appeal to today’s homebuyers. Speed of construction stands out as a primary benefit, with significantly shorter timelines compared to traditional builds. Cost efficiency is another major draw, as factory production reduces labor costs, minimizes material waste, and allows bulk purchasing of supplies. Quality control improves through standardized manufacturing processes and multiple inspection points. Environmental benefits include reduced construction waste, improved energy efficiency, and less site disturbance. Financing for prefabricated homes has become more accessible as lenders increasingly recognize their value and durability. Additionally, modern prefabricated designs have shed outdated stereotypes, offering contemporary aesthetics that rival custom-built homes.
| Home Type | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Modular Home | Champion Home Builders | $80,000 - $200,000 |
| Panelized Home | Lindal Cedar Homes | $150,000 - $400,000 |
| Manufactured Home | Clayton Homes | $50,000 - $120,000 |
| Custom Prefab | Blu Homes | $200,000 - $500,000 |
| Tiny Prefab Home | Tumbleweed Houses | $40,000 - $90,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Conclusion
Prefabricated homes represent a practical and increasingly popular alternative to traditional construction, offering faster build times, controlled quality, and potential cost savings. With diverse design options, customization possibilities, and improved financing availability, prefabrication addresses many challenges facing modern homebuyers. Understanding local regulations, comparing manufacturers, and carefully planning customization choices are essential steps toward successfully purchasing a prefabricated home. As the housing market evolves, prefabrication continues to demonstrate its value as an efficient, sustainable, and affordable housing solution.