Understanding Testosterone Supplements for Men: Informative Guide to Choices
In 2026, American men exploring testosterone supplements face a range of options varying in formulation and regulatory compliance. Understanding ingredient profiles, manufacturing standards, and regulatory considerations is essential to making informed decisions about these products within men’s health.
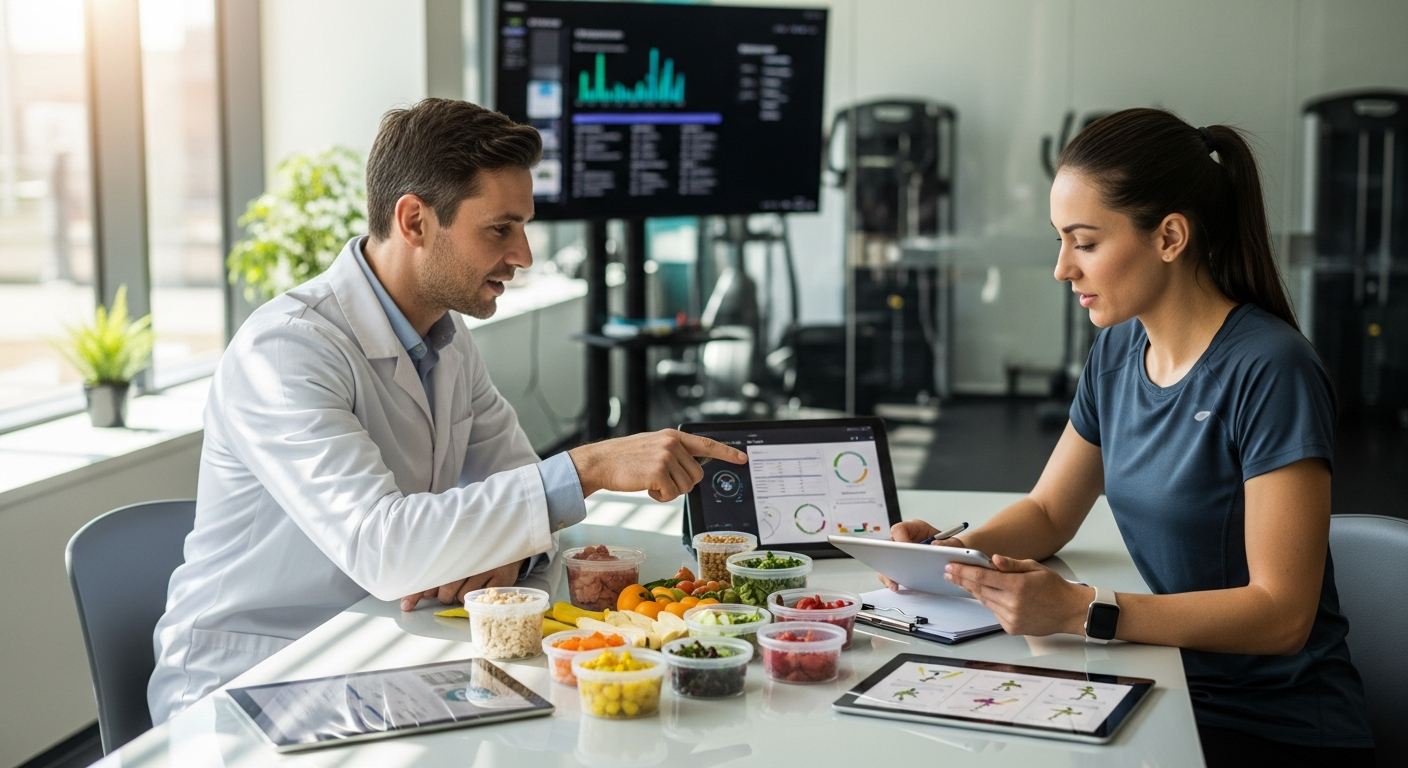

Testosterone plays a crucial role in male health, influencing everything from muscle development and bone density to mood and energy levels. As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, leading many to explore supplementation options. The market offers numerous products claiming to boost testosterone naturally, but understanding their composition, effectiveness, and safety considerations is vital before incorporating them into your routine.
Which Ingredients Appear in Testosterone Boosters?
Testosterone boosters typically contain a blend of vitamins, minerals, and herbal extracts believed to support natural testosterone production. Common ingredients include D-aspartic acid, an amino acid that may influence hormone production in the body. Fenugreek extract appears frequently in formulations, with some studies suggesting it may help maintain healthy testosterone levels. Zinc and magnesium are essential minerals that play roles in hormone regulation and often appear in these supplements.
Vitamin D3 has gained attention for its potential relationship with testosterone levels, particularly in individuals with deficiencies. Tribulus terrestris, an herbal extract, remains popular despite mixed scientific evidence regarding its effectiveness. Other common ingredients include ashwagandha, an adaptogenic herb that may help reduce stress-related hormone imbalances, and DHEA, a hormone precursor that converts to testosterone in the body. Ginger extract, boron, and various other plant compounds round out typical formulations, each claiming specific benefits for male hormonal health.
How to Evaluate American-Made Supplement Quality
Evaluating supplement quality requires attention to several key factors. Third-party testing certifications from organizations like NSF International, USP, or ConsumerLab provide independent verification of product contents and purity. These certifications indicate that supplements have been tested for contaminants and contain the ingredients listed on labels in stated amounts.
Manufacturing practices matter significantly. Look for products made in facilities following Good Manufacturing Practices, which ensure quality control throughout production. Transparency in labeling is another important consideration. Quality manufacturers provide complete ingredient lists with specific amounts rather than hiding behind proprietary blends. The presence of contact information, batch numbers, and expiration dates indicates responsible manufacturing.
Researching company reputation through customer reviews, industry standing, and history of recalls or warnings provides additional insight. American-made supplements must comply with FDA regulations for dietary supplements, though these standards differ from pharmaceutical requirements. Checking whether companies voluntarily submit to additional testing and maintain transparency about sourcing and manufacturing processes helps distinguish quality products from questionable ones.
Natural Boosters vs Clinical Testosterone Therapy
Natural testosterone boosters and clinical testosterone therapy represent fundamentally different approaches to addressing low testosterone. Natural supplements contain ingredients that may support the body’s own testosterone production, working indirectly through nutritional support and herbal compounds. These products are available over-the-counter without prescriptions and are regulated as dietary supplements rather than medications.
Clinical testosterone therapy involves prescription medications containing synthetic or bioidentical testosterone administered through injections, gels, patches, or pellets. This medical treatment directly replaces or supplements testosterone in the body and requires physician supervision, regular blood testing, and monitoring for side effects. Testosterone therapy is prescribed for diagnosed hypogonadism, a medical condition characterized by significantly low testosterone levels confirmed through blood tests.
The effectiveness differs substantially between these approaches. Clinical therapy provides predictable, measurable increases in testosterone levels, while natural supplements show variable and often modest effects in research studies. Natural boosters may benefit individuals with borderline levels or nutritional deficiencies, but they cannot replicate the results of medical testosterone replacement. The decision between these options depends on actual testosterone levels, underlying health conditions, and medical necessity rather than personal preference alone.
Safety Checks: Banned Substances and Fillers
Safety concerns surrounding testosterone supplements include the potential presence of banned substances, undisclosed ingredients, and harmful fillers. Some products have been found to contain actual anabolic steroids or pharmaceutical compounds not listed on labels, posing serious health risks and potential legal issues for users. The FDA occasionally issues warnings about specific supplements found to contain hidden drug ingredients.
Contaminants and fillers present another concern. Heavy metals, pesticides, and other toxins may appear in poorly manufactured supplements. Some products contain excessive amounts of certain ingredients or include fillers that may cause allergic reactions or digestive issues. Artificial colors, preservatives, and binding agents vary in quality and safety across different brands.
Verifying product safety involves checking FDA warning letters and recalls, reviewing third-party testing results, and researching whether products have been flagged by regulatory agencies or consumer protection organizations. Athletes should be particularly cautious, as some testosterone boosters contain substances banned by sports organizations. Reading labels carefully for allergen warnings and researching unfamiliar ingredients helps avoid potential adverse reactions.
When to Talk With Your Physician First
Consulting a healthcare professional before starting testosterone supplements is essential in several situations. Men experiencing symptoms potentially related to low testosterone, such as persistent fatigue, decreased libido, mood changes, or difficulty building muscle despite exercise, should undergo proper medical evaluation before self-treating. Blood tests can determine actual testosterone levels and identify whether symptoms stem from hormonal issues or other medical conditions.
Individuals with existing health conditions, particularly prostate issues, heart disease, sleep apnea, or blood clotting disorders, must discuss supplement use with their physicians. Testosterone supplements may interact with medications or exacerbate certain conditions. Men taking blood thinners, diabetes medications, or corticosteroids should seek medical guidance, as interactions may occur.
Age considerations matter as well. Older men and those with multiple health conditions face higher risks from unsupervised supplementation. Anyone considering testosterone supplements should discuss their complete medical history, current medications, and health goals with a qualified healthcare provider who can offer personalized recommendations based on individual circumstances rather than marketing claims.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Understanding testosterone supplements requires careful consideration of ingredients, quality standards, and individual health needs. While these products may offer benefits for some men, they are not appropriate or effective for everyone. Distinguishing between marketing claims and scientific evidence, recognizing when medical intervention is necessary, and prioritizing safety through quality evaluation and professional consultation ensures responsible decision-making regarding male hormonal health.